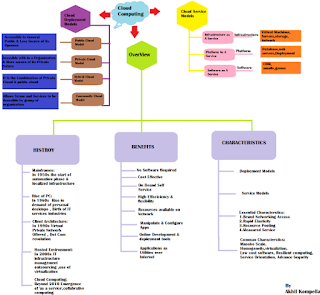
Introduction To Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing provides us with a means of accessing the applications as utilities over the Internet. It allows us to create, configure, and customize the applications online.
What is Cloud?
The term Cloud refers to
a Network or Internet. In other words, we can say that Cloud is something,
which is present at remote location. Cloud can provide services over public and
private networks, i.e., WAN, LAN or VPN.
Applications such as
e-mail, web conferencing, customer relationship management (CRM) execute on
cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing refers
to manipulating, configuring, and accessing the hardware and software resources
remotely. It offers online data storage, infrastructure, and application.
Cloud computing offers platform
independence, as the software is not required to be installed locally on the
PC. Hence, Cloud Computing is making our business applications mobile and
collaborative.
Basic Concepts
There are certain services
and models working behind the scene making cloud computing feasible and
accessible to end users. The following are the working models for cloud computing:
●
Deployment Models
●
Service Models
Deployment Models:
Public Cloud
The public cloud allows
systems and services to be easily accessible to the general public. Public
clouds may be less secure because of their openness.
Private Cloud
The private cloud allows
systems and services to be accessible within an organization. It is more
secure because of its private nature.
Community
Cloud
The community cloud
allows systems and services to be accessible by a group of organizations.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is a
mixture of public and private cloud, in which the critical activities are
performed using private cloud while the non-critical activities are performed
using public cloud.
Service Models
Cloud computing is based
on service models. These are categorized into three basic service models which
are -
●
Infrastructure-as–a-Service
(IaaS)
●
Platform-as-a-Service
(PaaS)
●
Software-as-a-Service
(SaaS)
Anything-as-a-Service
(XaaS) is yet another service model, which includes Network-as-a-Service,
Business-as-a-Service, Identity-as-a-Service, Database-as-a-Service or
Strategy-as-a-Service.
The infrastructure-as-a-Service
(IaaS) is the most basic level of service. Each of the service models inherits the security and management mechanism from the underlying model, as shown in
the following diagram:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides access to
fundamental resources such as physical machines, virtual machines, virtual
storage, etc.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides the
runtime environment for applications, development and deployment tools, etc.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS model allows to use
software applications as a service to end-users.
History of Cloud
Computing
The concept of Cloud
Computing came into existence in the year 1950 with implementation of mainframe
computers, accessible via thin/static clients. Since then, cloud computing has
been evolved from static clients to dynamic ones and from software to services.
The following diagram explains the evolution of cloud computing:
Benefits
Cloud Computing has
numerous advantages. Some of them are listed below -
●
One can access
applications as utilities, over the Internet.
●
One can manipulate and
configure the applications online at any time.
●
It does not require to
install a software to access or manipulate cloud application.
●
Cloud Computing offers
online development and deployment tools, programming runtime environment through
PaaS model.
●
Cloud resources are
available over the network in a manner that provide platform independent access
to any type of clients.
●
Cloud Computing offers
on-demand self-service. The resources can be used without interaction with
cloud service provider.
●
Cloud Computing is
highly cost effective because it operates at high efficiency with optimum
utilization. It just requires an Internet connection
●
Cloud Computing offers
load balancing that makes it more reliable.
Risks related to Cloud
Computing
Although cloud Computing
is a promising innovation with various benefits in the world of computing, it
comes with risks. Some of them are discussed below:
Security and Privacy
It is the biggest
concern about cloud computing. Since data management and infrastructure
management in cloud is provided by third-party, it is always a risk to handover
sensitive information to cloud service providers.
Although cloud computing vendors ensure highly secured password protected accounts, any sign
of security breach may result in loss of customers and businesses.
Lock In
It is very difficult for
the customers to switch from one Cloud Service Provider (CSP) to another. It
results in dependency on a particular CSP for service.
Isolation Failure
This risk involves the
failure of isolation mechanism that separates storage, memory, and routing
between the different tenants.
Management Interface
Compromise
In the case of public cloud
provider, the customer management interfaces are accessible through the
Internet.
Insecure or Incomplete
Data Deletion
It is possible that the
data requested for deletion may not get deleted. It happens because either of
the following reasons
●
Extra copies of data are
stored but are not available at the time of deletion
●
Disk that stores data of
multiple tenants is destroyed
Characteristics of Cloud
Computing
On Demand Self Service
Cloud Computing allows
the users to use web services and resources on demand. One can log on
to a
website at any time and use them.
Broad Network Access
Since cloud computing is
completely web based, it can be accessed from anywhere and at any time.
Resource Pooling
Cloud computing allows
multiple tenants to share a pool of resources. One can share a single physical
instance of hardware, database and basic infrastructure.
Rapid Elasticity
It is very easy to scale
the resources vertically or horizontally at any time. Scaling of resources
means the ability of resources to deal with increasing or decreasing demand.
The resources being used
by customers at any given point of time are automatically monitored.
Measured Service
In this service cloud
provider controls and monitors all the aspects of cloud service. Resource
optimization, billing, and capacity planning etc. depend on it.
Best Regards,
Akhil Kompella
Well structure and organized information
ReplyDelete